
If the fossil has 35 of its carbon 14 still, then we can substitute values into our equation. Where t 1/2 is the half-life of the isotope carbon 14, t is the age of the fossil (or the date of death) and ln () is the natural logarithm function. Increasingly though, students are learning about the principles of radiocarbon dates in archaeology, palaeontology and climate science degrees and can combine cross-disciplinary studies. We can use a formula for carbon 14 dating to find the answer.
#Carbon 14 dating calculator free
Typically, a Master's Degree in chemistry is required because of the extensive lab work. Completely free carbon dating links: carbon 14 dating calculator to show the subsequent calculation must then used the equation f t. There are a number of ways to enter into a career in studying radiocarbon dating. Stone and metal cannot be dated but pottery may be dated through surviving residue such as food particles or paint that uses organic material (8). The above list is not exhaustive most organic material is suitable so long as it is of sufficient age and has not mineralised - dinosaur bones are out as they no longer have any carbon left.

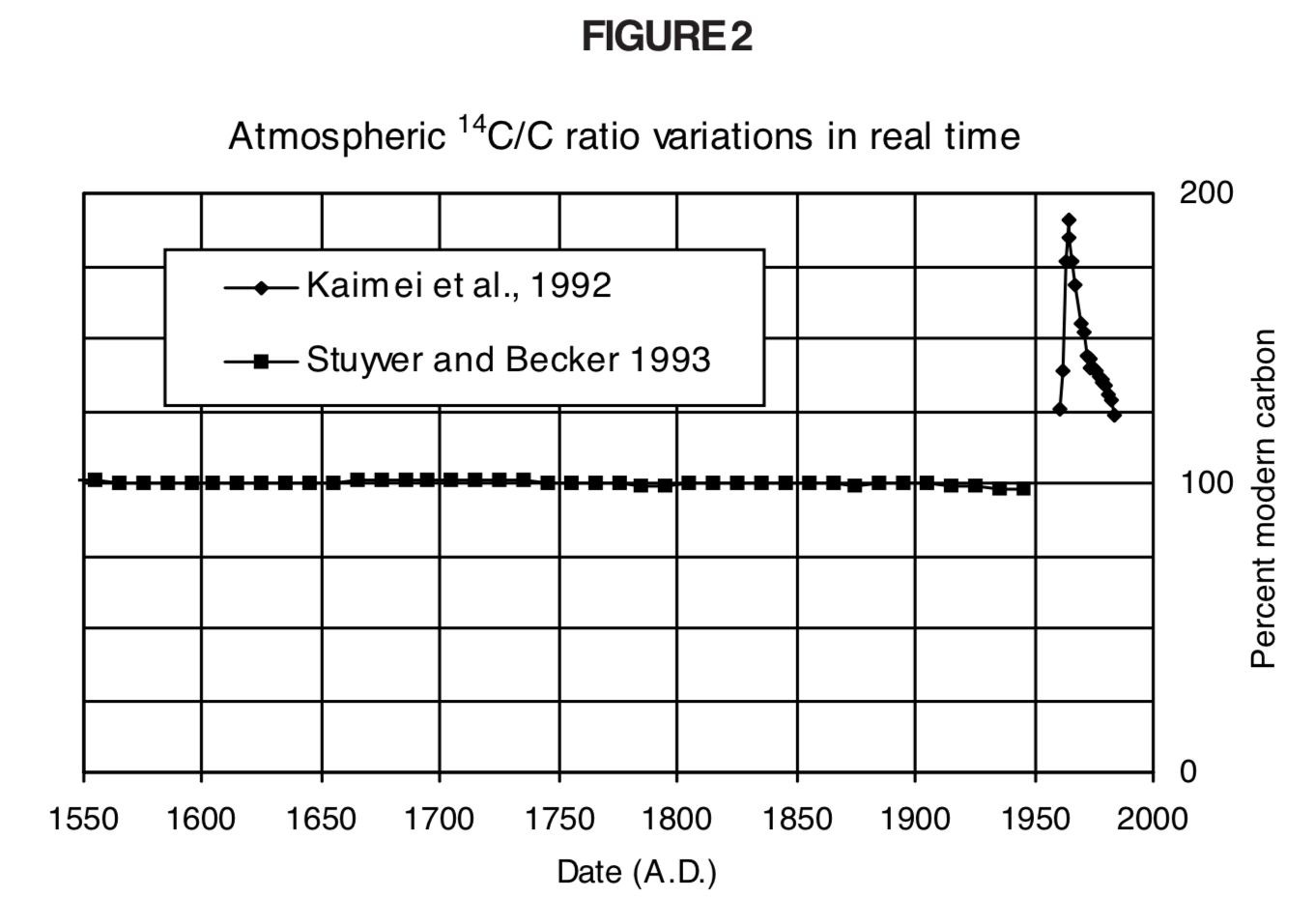
It also has some applications in geology its importance in dating organic materials cannot be underestimated enough. Today, the radiocarbon-14 dating method is used extensively in environmental sciences and in human sciences such as archaeology and anthropology. After this point, other Absolute Dating methods may be used. The half-life of the 14C isotope is 5,730 years, adjusted from 5,568 years originally calculated in the 1940s the upper limit of dating is in the region of 55-60,000 years, after which the amount of 14C is negligible (3).

The other two isotopes in comparison are more common than carbon-14 in the atmosphere but increase with the burning of fossil fuels making them less reliable for study (2) carbon-14 also increases, but its relative rarity means its increase is negligible. The unstable nature of carbon 14 (with a precise half-life that makes it easy to measure) means it is ideal as an absolute dating method. There are three carbon isotopes that occur as part of the Earth's natural processes these are carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14. The other method is “Relative Dating” which gives an order of events without giving an exact age (1): typically artefact typology or the study of the sequence of the evolution of fossils. Despite the name, it does not give an absolute date of organic material - but an approximate age, usually within a range of a few years either way. This relationship enables the determination of all values, as long as at least one is known.Radiocarbon dating is a method of what is known as “Absolute Dating”. Using the above equations, it is also possible for a relationship to be derived between t 1/2, τ, and λ. Derivation of the Relationship Between Half-Life Constants This means that the fossil is 11,460 years old. If an archaeologist found a fossil sample that contained 25% carbon-14 in comparison to a living sample, the time of the fossil sample's death could be determined by rearranging equation 1, since N t, N 0, and t 1/2 are known. N t is the remaining quantity after time, t The carbon-14 undergoes radioactive decay once the plant or animal dies, and measuring the amount of carbon-14 in a sample conveys information about when the plant or animal died.īelow are shown three equivalent formulas describing exponential decay: It is incorporated into plants through photosynthesis, and then into animals when they consume plants. The process of carbon-14 dating was developed by William Libby, and is based on the fact that carbon-14 is constantly being made in the atmosphere.
The half-life of carbon-14 is approximately 5,730 years, and it can be reliably used to measure dates up to around 50,000 years ago.
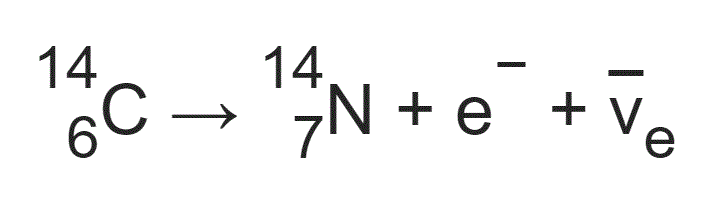
One of the most well-known applications of half-life is carbon-14 dating. The term is most commonly used in relation to atoms undergoing radioactive decay, but can be used to describe other types of decay, whether exponential or not. Half-life is defined as the amount of time it takes a given quantity to decrease to half of its initial value.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
